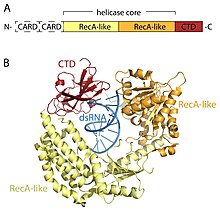
Structural Basis for the Activation of Innate Immune Pattern-Recognition Receptor RIG-I by Viral RNA: Cell
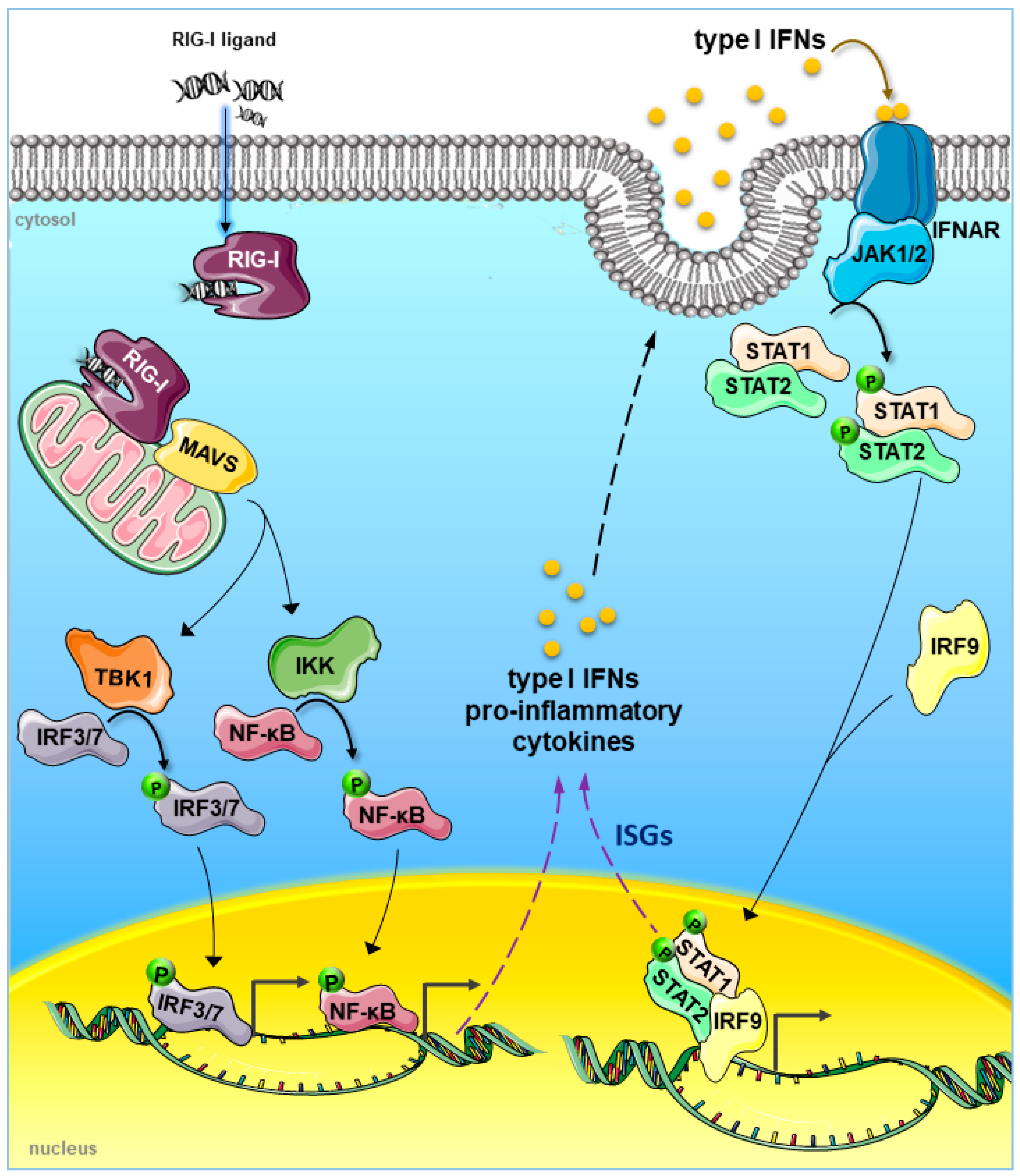
Cancers | Free Full-Text | The Innate Immune Signalling Pathways: Turning RIG-I Sensor Activation against Cancer

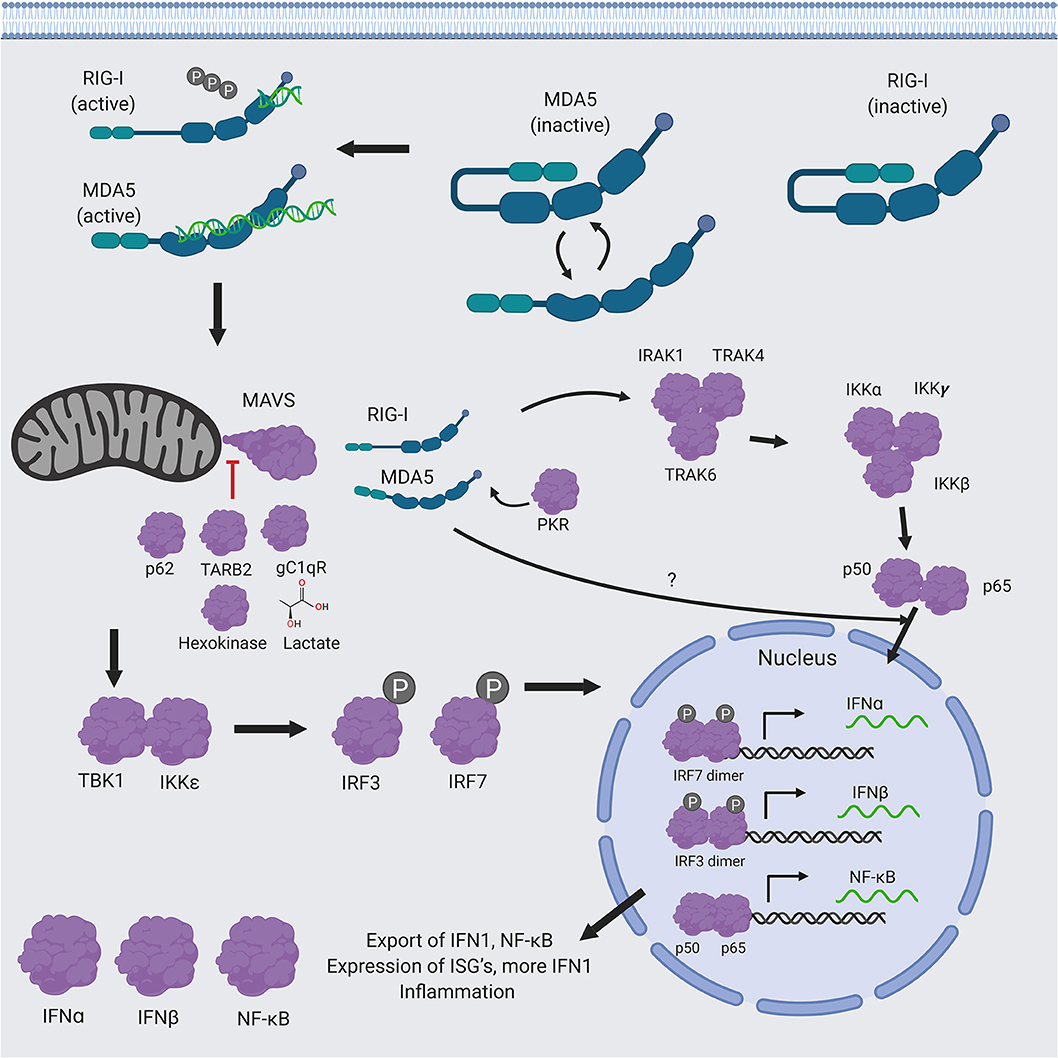
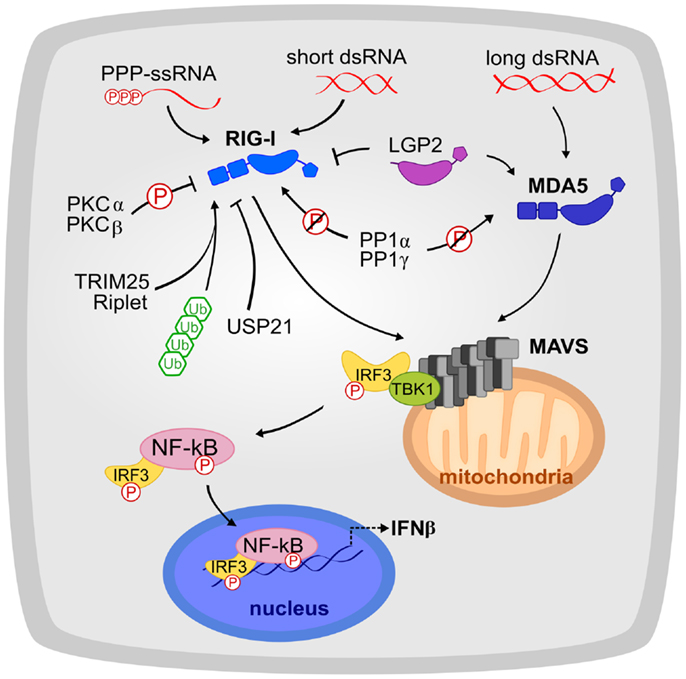
Regulation of retinoic acid-inducible gene-i (RiG-i) activation. (a)... | Download Scientific Diagram

RIG-I-induced innate antiviral immunity protects mice from lethal SARS-CoV-2 infection: Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids
HSCARG Negatively Regulates the Cellular Antiviral RIG-I Like Receptor Signaling Pathway by Inhibiting TRAF3 Ubiquitination via Recruiting OTUB1 | PLOS Pathogens

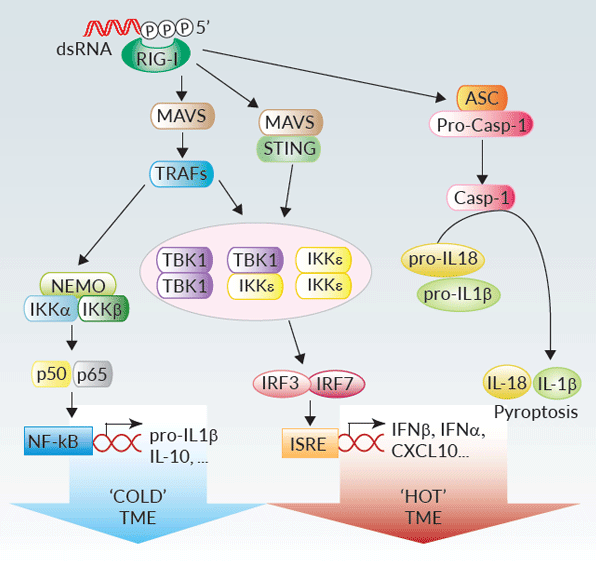
Signaling through RIG-1 like Receptors in lupus. Following recognition... | Download Scientific Diagram

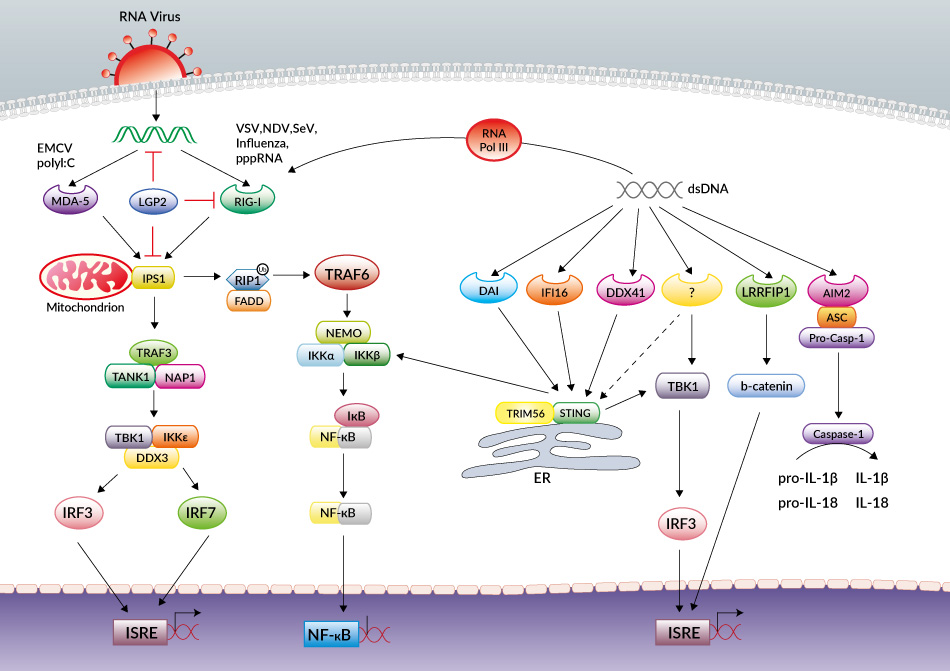
Viruses | Free Full-Text | Viral Evasion of RIG-I-Like Receptor-Mediated Immunity through Dysregulation of Ubiquitination and ISGylation

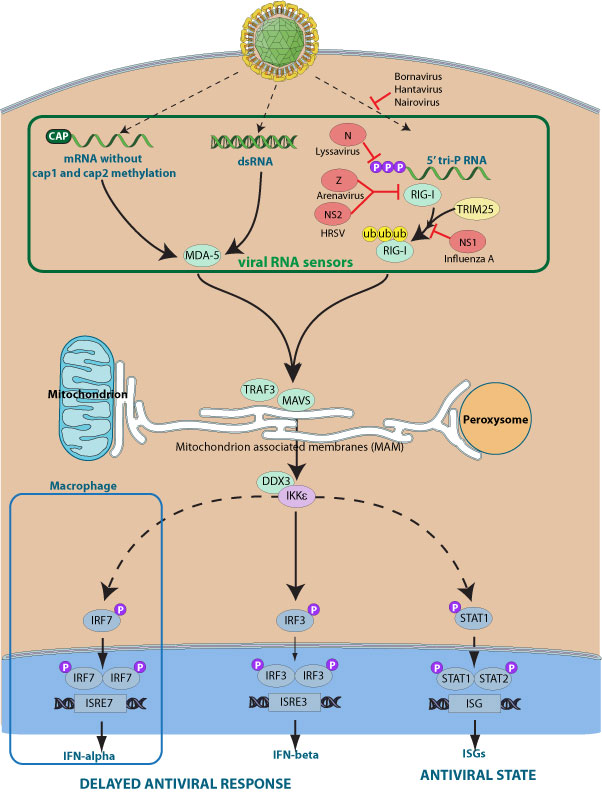
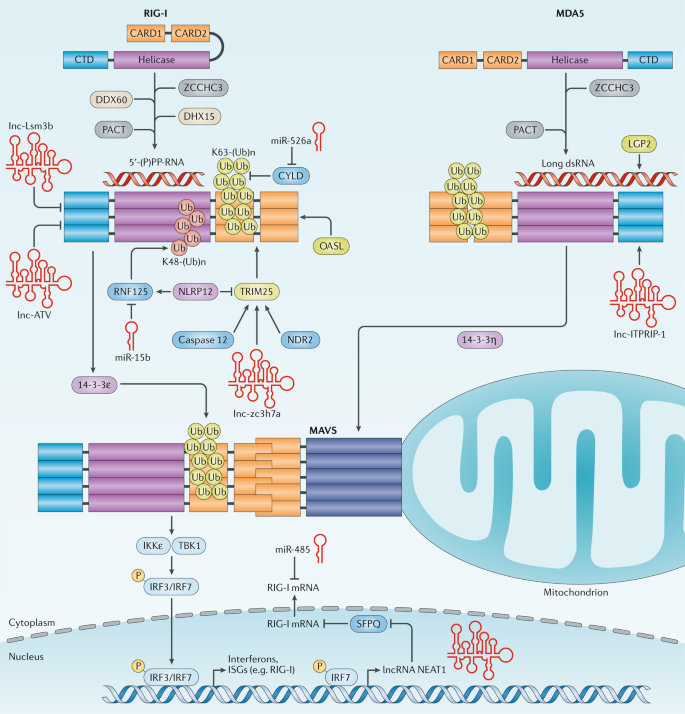
Regulation of RIG-I-like receptor-mediated signaling: interaction between host and viral factors | Cellular & Molecular Immunology